Price to Earnings Ratio - ("P/E Ratio")
Price to Earnings Ratio = Market Value per Share ÷ Earnings per Share
One of the most widely used ratios, it compares the current price with earnings to see if a stock is over or under valued.
Things to remember
- Generally a high P/E ratio means that investors are anticipating higher growth in the future.
- The average market P/E ratio is 20-25 times earnings.
- Estimated earnings can be used to calculate the projected P/E ratio.
- Companies that are losing money do not have a P/E ratio.
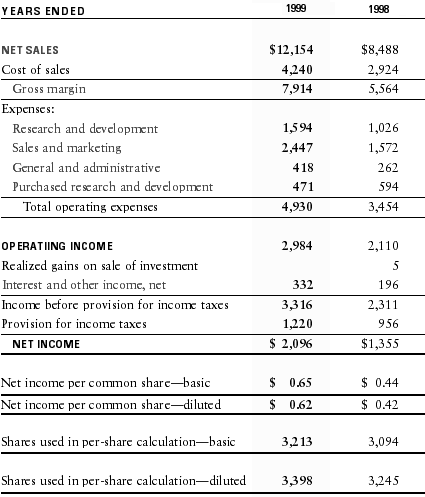
For Cory's Tequila Co. ($107.125 ÷$0.65) = 164.8
Price-Earnings Analysis:
Sometimes referred to as the P/E multiple, the idea behind the P/E ratio is that it is a prediction or more likely an expectation of the company's performance in the future. The P/E ratio for the overall market averages around 20, so as you can see Cory's Tequila Co. is much higher than this. In other words the market is expecting big things from Cory's Tequila Co. in the future.
One thing to remember is that if a company has a low P/E ratio it doesn't necessarily mean that it is undervalued. The P/E doesn't dictate the stock price. In fact a low P/E could mean that the company's earning are flat or growing slowing. They could also be in financial trouble. On its own, the P/E ratio doesn't tell a whole lot, but it's useful to compare the P/E ratios of other companies in the same industry, or to the market in general, or against the company's own historical P/E ratio.
